Praktikum Biophysikalische Chemie: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
* Use a text editor to write a new file, vaso.upl, that contains the upper distance bounds derived from NOESY cross peaks, using the [[standard CYANA nomenclature]] for atoms in proteins and the same format as in the following example: | * Use a text editor to write a new file, vaso.upl, that contains the upper distance bounds derived from NOESY cross peaks, using the [[Image:CyanaNomenclature.png|standard CYANA nomenclature]] for atoms in proteins and the same format as in the following example: | ||
91 THR HB 93 GLN QB 5.50 | 91 THR HB 93 GLN QB 5.50 | ||
Revision as of 18:01, 9 January 2009
Download the course material:
Store the file PBCPraktikumCyana.tgz in your home directory.
Unpack the data
tar zxf PBCPraktikumCyana.tgz
Run the setup command
setup_cyana
- Make a new directory for the structure calculation, and change into it:
mkdir vaso cd vaso
- Use a text editor to write a new file, vaso.seq, that contains the peptide sequence, one upper-case residue name per line, given in the standard three-letter code for amino acids (except for cysteine residues that are involved in a disulfide bond, which are denoted by "CYSS"), e.g.
CYSS TYR PHE GLN ASN CYSS PRO ARG GLY
- Use a text editor to write a new initialization script, init.cya, for the program CYANA with the following content:
cyanalib read seq vaso.seq
- These two commands will be executed automatically whenever the program CYANA is started. The cyanalib command reads the standard residue library of CYANA, and the command read seq vaso.seq reads the polypeptide sequence.
- Use a text editor to write a new file, vaso.upl, that contains the upper distance bounds derived from NOESY cross peaks, using the
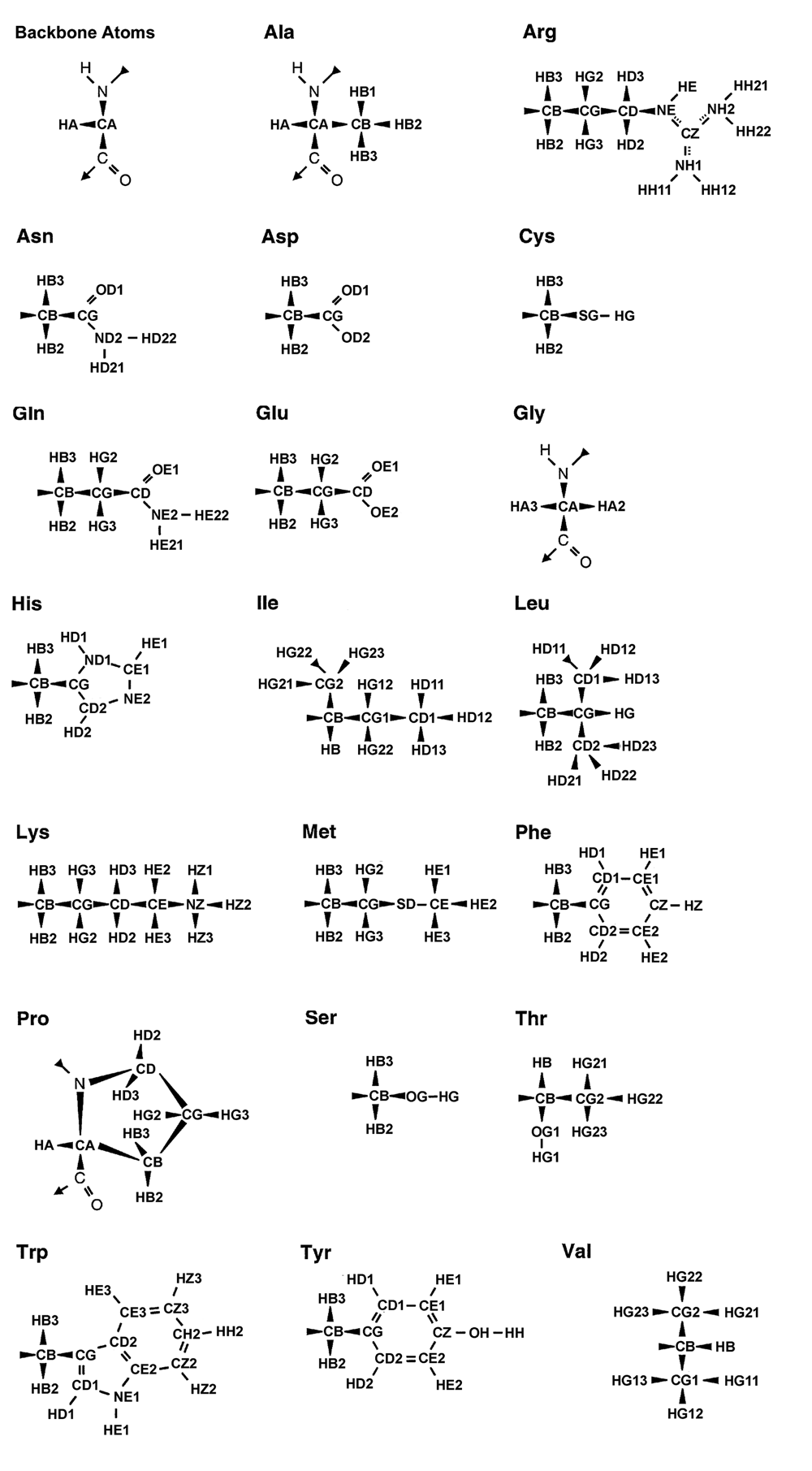 for atoms in proteins and the same format as in the following example:
for atoms in proteins and the same format as in the following example:
91 THR HB 93 GLN QB 5.50 80 SER HB2 81 ILE H 4.22 80 SER HB3 81 ILE H 4.22 81 ILE HA 84 LEU H 4.01 81 ILE HA 84 LEU HB2 4.47 81 ILE HA 81 ILE QG2 3.46 81 ILE HA 81 ILE HG12 3.77 28 VAL HA 39 LEU HG 3.97 52 SER H 52 SER HB2 3.96 52 SER H 52 SER HB3 3.96 99 SER QB 101 VAL H 5.50 43 SER H 43 SER QB 3.12 43 SER QB 48 GLU H 4.07 42 GLU HA 43 SER QB 5.50 43 SER QB 48 GLU HB2 3.95
- The exact number of spaces between different items is irrelevant, but the "TAB" key should not be used. The Degenerate groups of atoms, e.g. methyl groups, and diastereotopic pairs of hydrogen atoms, e.g. HB2/HB3 in serine, are referred to by "pseudoatoms" whose names start with "Q"